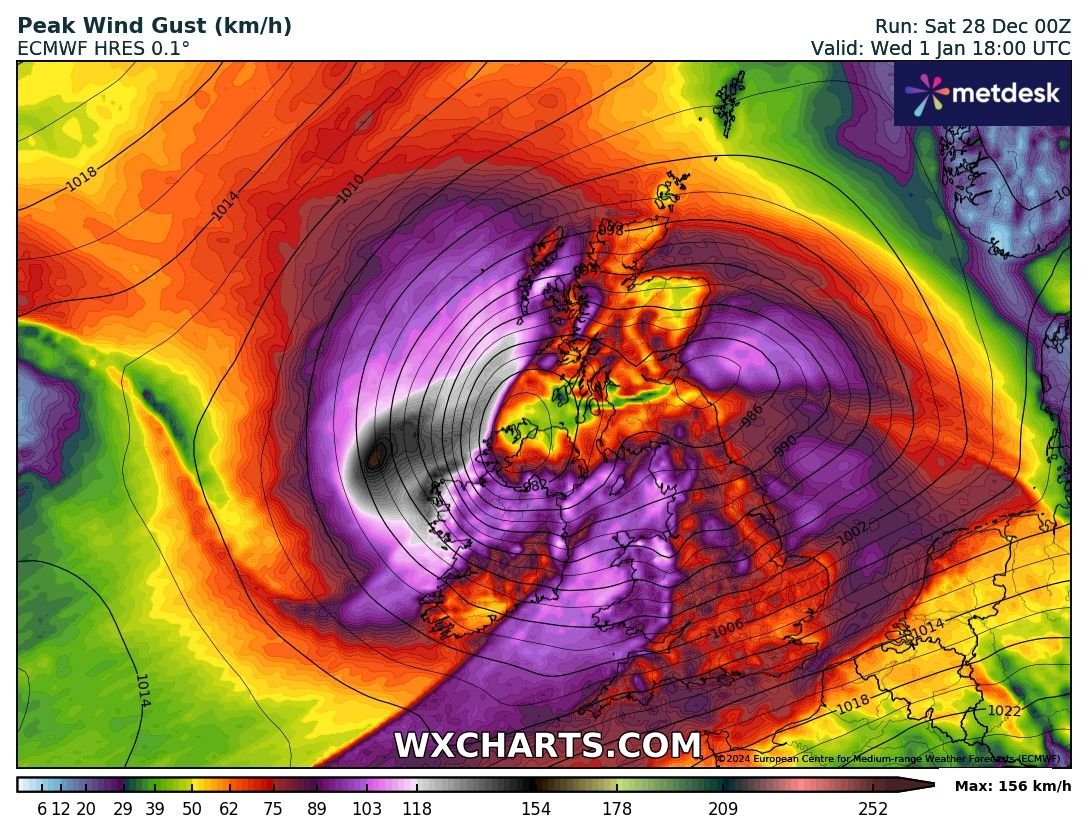
Warning for beach-goers this weekend as dangerous Portuguese man o war spotted on Irish Beaches
Portuguese man o war jelly
There have been sightings of the jellyfish-like Portuguese man o' war on some beaches in County Clare.
The creatures, which resemble jellyfish but are a species of siphonophore, cause painful stings if people come in contact with their tentacles.
They can be fatal for those who may suffer a severe reaction.
Sightings have been reported at Fanore, Lahinch, Doughmore, Doonbeg and Kilkee beaches
Jellyfish are common on Irish beaches but the man o' war is rare in colder North Atlantic waters. They can be swept in by the wind.
It comes a month after a sighting in Northern Ireland on the West Strand beach in Portrush, County Antrim.
Stormont’s Department of Agriculture Environment and Rural Affairs (Daera) warned people to avoid contact with them.
County Clare’s water safety development officer Clare McGrath confirmed sightings of the deadly species.
She said that lifeguards are on the lookout for them on the county's beaches and can get rid of them.
But she also appealed to people to be informed and vigilant about touching them.
"I'd be more worried about children and pets who are very curious and who are walking on the beach," Ms McGrath told RTÉ .
"These siphonophores are quite distinctive and have this bluish balloon like float on their bodies, and children may be attracted to them and might poke them.
"And animals may also be inclined to approach them. Swimmers will see them instantly with their blue balloon in the water and can stay away from them.
"People should inform the lifeguards of their presence if they see them.
"If they get stung people should remove or scrape the tentacles free with something like a credit card and clean their skin with sea water to flush out the toxins."
There are five native jellyfish species in Ireland:
Barrel
Blue
Common (Moon)
Compass
Lion’s Mane
A sixth type (Pelagia noctiluca) occasionally makes an appearance in Irish coastal waters. There have been rare reported sightings of the Portuguese Man O’War in Irish waters. The Portuguese Man O’War is not a true jellyfish but is closely related to the jellyfish family and can give a bad sting. The Lion’s Mane is the most serious jellyfish in Irish waters.
View the Jellyfish ID Card below.
NICE SUMMER SUNSHINE & TEMPERATURES SET TO RISE AS HIGH AS 26C OR 27C THIS WEEKEND
〰️
NICE SUMMER SUNSHINE & TEMPERATURES SET TO RISE AS HIGH AS 26C OR 27C THIS WEEKEND 〰️
JELLYFISH STINGS
All jellyfish possess stinging cells, “stingers”, on their tentacles. Brushing against tentacles can cause the release of these stingers which contain venom (poison). Depending on the type of jellyfish, the stingers may not be sharp enough and long enough to pierce the skin and the skin forms a natural barrier to most stings. More delicate areas, such as the eyes and lips, might be more easily pierced.
However, the Lion’s Mane stinging cells are much sharper and can pierce skin easily resulting in a painful sting. Jellyfish stings in Ireland are not usually life threatening and just require basic first aid (see below) and simple pain relief.
RISK OF GETTING STUNG
Your risk of getting stung is increased if you:
touch jellyfish, so make sure curious children don’t get too close
swim at times when jellyfish appear in large numbers (a jellyfish bloom)
swim in a place known to have many jellyfish, especially on a downwind shore
swim or dive in jellyfish areas without protective clothing
play or sunbathe where jellyfish are washed up on the beach
Animals are also at risk of getting stung, therefore keep your dog on a lead when walking on the beach.
SYMPTOMS OF A JELLYFISH STING
Symptoms depend on the:
type of jellyfish
size of the sting
number of stingers released
amount of poison released
person's own sensitivity to the venom
person's general health status
Most symptoms will be mild and local to the sting area such as:
immediate stinging pain at the site of the sting
skin reactions such as redness and itching which can start immediately after being stung or sometime after the sting
More severe symptoms can include:
severe pain
long lasting pain
swelling of the affected area
significant and long lasting skin reactions
Serious sting reactions which require urgent medical attention
Very rarely a person might have a serious allergic reaction to a sting – breathing difficulties, chest tightness, swelling of the lips, mouth or tongue.
Serious generalised reactions to a jellyfish sting are more common in countries with highly poisonous jellyfish, such as the Box jellyfish.
A sting from a Lion’s Mane jellyfish can cause nausea, sweating, cramps, headaches and other symptoms.
A sting from a Pelagia noctiluca (only occasionally found in Irish waters) can cause dizziness, vomiting, diarrhoea, difficulty breathing and other symptoms.
A sting from the Portuguese Man O’War (rarely seen in Irish waters) can cause symptoms such as muscle spasms, headaches, diarrhoea, difficulty breathing, heart rhythm problems and other symptoms.
If in doubt seek medical attention.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU HAVE BEEN STUNG
Remove yourself from the water / vicinity of the jellyfish
If helping someone else make sure you don’t get stung yourself
Seek help and advice from lifeguards if you are on a lifeguarded beach
Try to carefully remove any attached tentacles by
flushing the sting area with sea water
removing tentacles with gloved hands, clean stick, tweezers, or scraping gently with the edge of a credit card. Don’t try to rub them off.
Mild symptoms of pain and swelling can be treated with simple painkillers such as paracetamol and ibuprofen
Mild itching at the sting site may respond to anti-histamine creams
Apply a 'dry cold pack' to the area (i.e. place a cold pack or ice inside a plastic bag and then wrap this package in a t-shirt or other piece of cloth)
Use HOT WATER for Portuguese Man O'War stings at approximately 45° Celsius for 20 minutes
Keep any puncture wounds clean and dry to avoid them getting infected
Seek medical attention if you develop any serious symptoms
WHAT NOT TO DO
Don’t rub the area
Don’t rinse with fresh water. Use seawater
Don’t urinate (pee) on the sting
Don’t use vinegar for the types of jellyfish stings that might happen in Ireland
Don’t use alcohol
Don’t put on a tight bandage